Mar 13, 2024
How Does a Motorcycle Engine Work?
How Does a Motorcycle Engine Work? Unveiling the Power Within
The rumble of a motorcycle engine ignites a sense of excitement and freedom. But have you ever wondered what goes on inside that powerful machine? Understanding how a motorcycle engine works unlocks the secrets behind its performance and empowers you to appreciate the intricate mechanics that propel you forward. This guide dives into the workings of a motorcycle engine, explaining each step of the process that transforms fuel and air into exhilarating power.
The Cycle of Power: A Four-Stroke Journey
The four-stroke cycle, the heart of most modern motorcycle engines, is a fascinating dance between air, fuel, combustion, and power generation. Let’s delve deeper into each stroke, exploring the intricate mechanics that transform a simple mixture into the thrilling force that propels you forward.
1. Intake Stroke: The Breath of Life
Imagine the piston at the top of the cylinder. As it moves down, a vacuum is created within the cylinder. This drop in pressure acts like a giant lung inhaling. But instead of air alone, a precisely measured air-fuel mixture rushes in through the open intake valve. This air-fuel mixture, a vital cocktail of oxygen and fuel, is the lifeblood of the engine.
2. Compression Stroke: Squeezing for Power
With the piston reaching the bottom of the cylinder, the intake valve slams shut. Now comes the squeeze play. The piston begins its upward journey, compressing the trapped air-fuel mixture. This compression significantly increases the pressure and temperature of the mixture, creating a potent energy source.
3. Combustion Stroke: The Spark of Excitement
The piston reaches the top of the compression stroke, and the stage is set for ignition. A spark plug, strategically positioned within the cylinder, unleashes a high-voltage spark. This spark ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid and violent explosion. The expanding hot gases generated by the combustion forcefully push the piston back down the cylinder.
4. Exhaust Stroke: Clearing the Stage
The force of the combustion pushes the piston down to its lowest point. As this happens, the exhaust valve opens, acting like an exhalation valve. The spent exhaust gases, now devoid of their energy potential, are pushed out of the cylinder through the open exhaust valve. With the exhaust valve closed and the piston returning upwards, the cycle begins anew, ready to repeat the dance of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
The Beauty of the Cycle: Efficiency and Power
The four-stroke cycle is a marvel of engineering efficiency. Each stroke plays a specific role, ensuring a continuous and controlled process. Unlike two-stroke engines, which combine intake and exhaust within a single stroke cycle, the four-stroke cycle allows for more complete combustion, leading to cleaner emissions and better fuel economy.
Beyond the Basics: Factors at Play
While the four-stroke cycle provides the core framework, several additional factors influence engine performance:
- Spark Plug Timing: The timing of the spark plug is crucial. A precisely timed spark ensures optimal combustion, maximizing power and efficiency.
- Valve Timing: The intake and exhaust valves must open and close at specific times during the cycle for efficient operation. The camshaft plays a critical role in controlling valve timing.
- Air-Fuel Ratio: The balance between air and fuel in the mixture significantly impacts performance and emissions. A proper air-fuel ratio ensures complete combustion, minimizing unburnt fuel and harmful emissions.
Understanding the four-stroke cycle is the first step to appreciating the intricate world of motorcycle engines. By delving deeper into these components and their interactions, you’ll gain a newfound respect for the engineering marvel that propels your motorcycle adventures.
Key Players in the Engine Drama: Essential Components
Several key components work together to ensure the smooth operation of a motorcycle engine:
-
Pistons: These cylindrical components move up and down within the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture and transferring the force of combustion into power.
-
Cylinders: Cylinders are the chambers where the pistons move. The engine block houses the cylinders, and their size and number significantly impact the engine’s power output.
-
Connecting Rods: Connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft, converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into the rotational motion of the crankshaft.
-
Crankshaft: The crankshaft is a rotating shaft that receives the force from the connecting rods and converts it into rotational power. This rotational power is ultimately used to drive the rear wheel of the motorcycle.
-
Valves: Intake valves allow the air-fuel mixture into the cylinders, while exhaust valves release the spent exhaust gases. These valves open and close at specific times during the engine cycle.
-
Camshaft: The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves using lobes that push on valve followers. The camshaft timing is crucial for optimal engine performance.
-
Spark Plug: The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the combustion stroke. A high-voltage spark jumps across the gap between the spark plug electrodes, initiating combustion.
-
Fuel Injection System: Modern motorcycles typically utilize fuel injection systems that precisely deliver the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. This ensures efficient combustion and optimal performance.
Fueling the Ride: The Power of Air and Fuel
The air-fuel mixture plays a vital role in engine operation. Air provides the oxygen necessary for combustion, while fuel provides the energy. A properly balanced air-fuel mixture ensures efficient combustion, leading to optimal power and fuel economy.
The fuel injection system precisely meters the amount of fuel injected into the intake air stream, creating the optimal air-fuel mixture. Sensors monitor various engine parameters like air pressure and temperature, allowing the fuel injection system to adjust the mixture for optimal performance under different conditions.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Considerations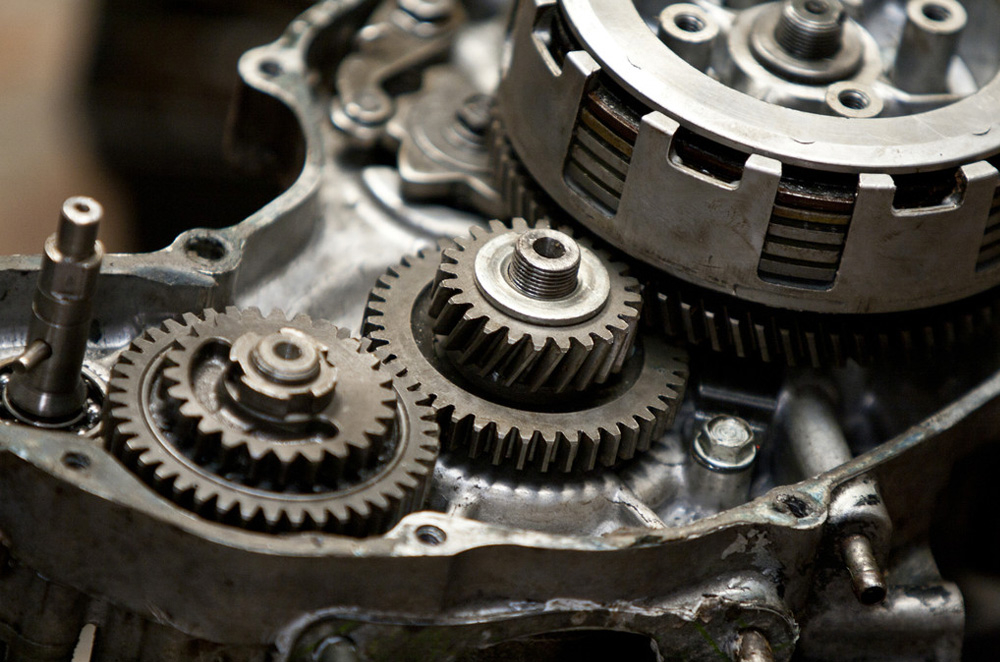
While the four-stroke cycle provides the foundation, some additional aspects influence engine operation:
-
Engine Displacement: Engine displacement refers to the total volume swept by all the pistons in an engine. A larger displacement engine typically produces more power, however, it also comes with increased weight and potentially lower fuel efficiency.
-
Cooling System: Motorcycle engines generate significant heat during operation. A cooling system, typically using liquid coolant or air, is essential to maintain optimal engine temperature and prevent overheating.
-
Lubrication System: A lubrication system ensures that moving parts within the engine are properly lubricated to minimize friction and wear. Engine oil plays a crucial role in this process.
Understanding Your Engine: A Key to a Smooth Ride
Knowing how your motorcycle engine works empowers you to appreciate its capabilities and maintain it properly. Regular maintenance, like oil changes and air filter cleaning, ensures smooth operation and extends the engine’s lifespan.
By understanding the basic principles, you can also identify potential problems based on unusual sounds or behavior.
More Details