Mar 5, 2025
Everything You Need to Know About Motorcycle Engine Types
The Basics of Motorcycle Engines
Before diving into the various motorcycle engine types, let’s cover the basics. Every motorcycle engine is a power unit. Its purpose is to convert fuel into motion. This magic happens through internal combustion. A mix of air and fuel burns in the engine’s cylinders. This process pushes the pistons. The pistons turn the crankshaft. The crankshaft sends power to the wheels.
Engines have a few key parts. These are the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. The number and arrangement of cylinders vary. That’s what defines the engine type. Most engines also have valves. They control the flow of fuel-air mix and exhaust gases. All these parts work together. They create the ride you feel on two wheels.
Every motorcycle engine also features a cooling system. It may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. The cooling system keeps the engine at the right temperature. Without it, the engine would overheat.
Lubrication is crucial too. Oil lubricates moving parts. This reduces wear and tear. It helps the engine run smooth.
Motorcycle engines come with different transmissions. The transmission turns the engine’s power into useful work. It ensures the wheels get the right amount of power. This is crucial at different speeds.
Remember, a motorcycle’s performance depends on its engine. Size, power, efficiency, and sound link back to engine type. As we explore the common motorcycle engine types, remember these basics. They are the foundation of how engines define the riding experience.
Common Types of Motorcycle Engines

Exploring motorcycle engine types helps you understand what powers your ride. Now, let’s dive into the common types seen on the road.
Single-Cylinder Engines
Single-cylinder engines are simple and compact. They’re known for their lightweight design. Often found in smaller bikes, they offer good fuel economy. These engines have one cylinder and one piston. This setup makes maintenance easier. They’re perfect for beginners or light off-road use. But they may vibrate more at high speeds due to only having one piston.
Parallel-Twin Engines
Parallel-twin engines have two cylinders side by side. These engines balance power with smooth operation. They’re more powerful than single-cylinders but still efficient. Parallel-twins are common in mid-range motorcycles. They provide a balance between speed and control, making them versatile.
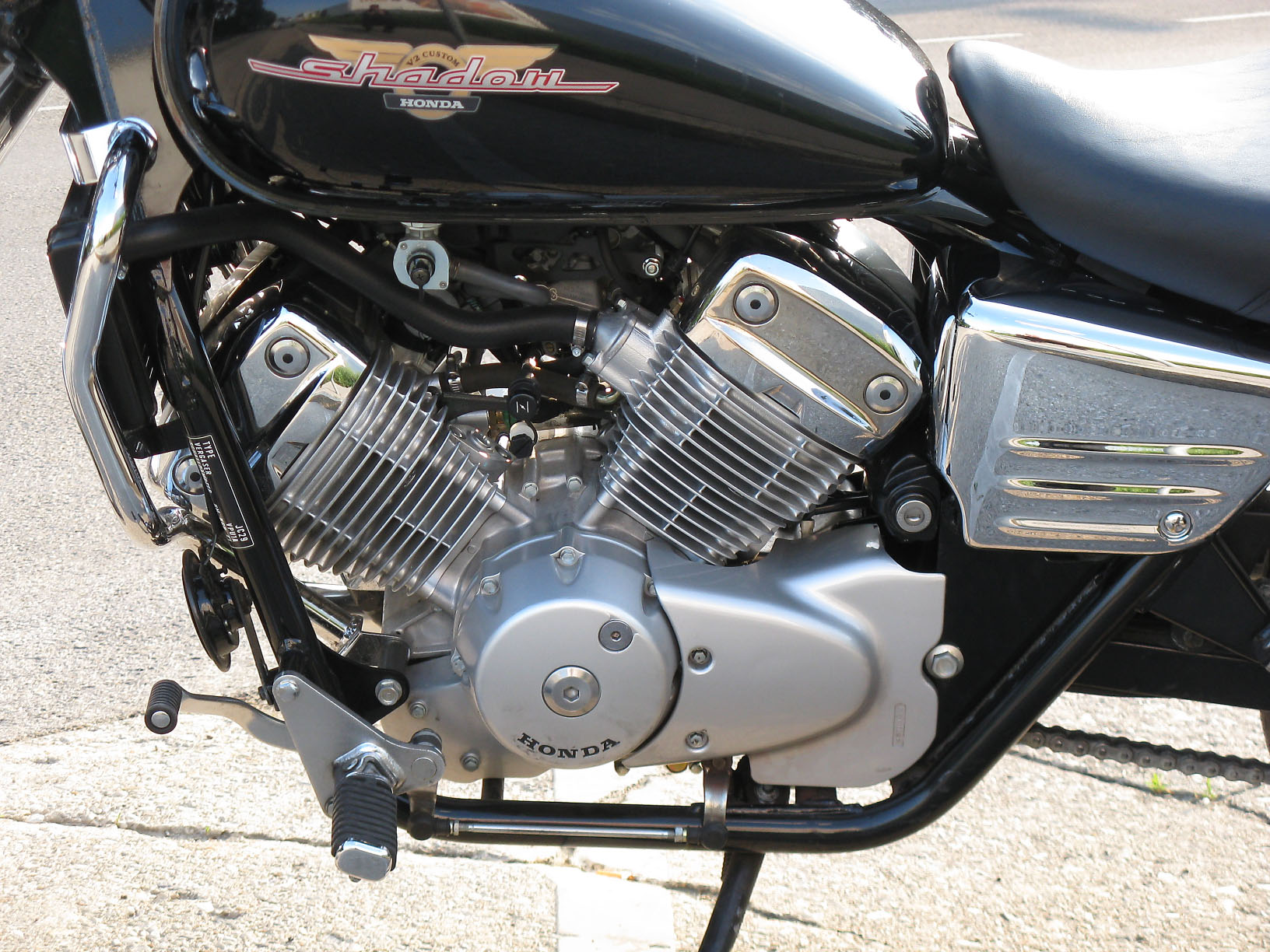
V-Twin Engines
V-twin engines have two cylinders in a ‘V’ shape. They’re known for their strong torque and distinctive rumble. These engines deliver power at low RPMs. That makes them popular in cruisers and touring bikes. V-twins offer a laid-back riding experience with plenty of pull.
Boxer Engines
Boxer engines have horizontally opposed cylinders. This design keeps the motorcycle’s center of gravity low. This results in better balance and handling. Known for durability, boxer engines are often found in adventure and touring bikes.
Inline-Four Engines
Inline-four engines feature four cylinders in a line. They’re known for high performance and smooth power delivery. Common in sportbikes, they can rev high and produce a lot of power. Inline-fours offer an exhilarating experience for thrill-seekers.
V4 Engines
V4 engines have four cylinders in a ‘V’ formation. This type combines the compact design of V-twins with the power of inline-fours. V4 engines are less common but offer superior balance and smoothness. They’re typically seen in high-end sport and touring motorcycles.
As you consider these motorcycle engine types, think about your riding needs. Each type impacts performance differently. The choice you make can define your motorcycle experience.
Characteristics of Different Engine Configurations

Each motorcycle engine type has its own set of characteristics that cater to different rider needs. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision about the type of motorcycle that’s right for you. Let’s look at what sets each engine configuration apart.
Single-Cylinder Engines
Single-cylinder engines, often referred to as “thumpers,” are ideal for their simplicity and ease of maintenance. Due to having only one cylinder, they are lightweight, which makes the motorcycle nimble and agile. They excel in fuel efficiency, which can be great for city commuting.
Parallel-Twin Engines
The parallel-twin configuration offers a step up in power and smoothness compared to single-cylinders. With two pistons moving parallel to each other, these engines can reduce vibrations, providing a more comfortable ride. They’re well-suited for everyday riders who enjoy a blend of performance and economy.
V-Twin Engines
Known for their deep, throaty sound, V-twin engines give a bike a lot of character. They have a good deal of low-end torque, making them easy to ride, especially in stop-and-go traffic. The unique layout also contributes to the bike’s overall aesthetic appeal.
Boxer Engines
The boxer engine’s horizontal configuration means a lower center of gravity and improved balance. This equates to more stable handling, especially in corners. These engines are often linked to long-lasting performance and rugged reliability.
Inline-Four Engines
Inline-four engines are all about high performance and high revs. They deliver smooth and predictable power, which is why they are a favorite amongst sportbike enthusiasts. With four cylinders in a straight line, they can generate a significant amount of horsepower.
V4 Engines
V4 engines offer a blend of the compact layout of the V-twin and the power output of inline-fours. They’re typically quieter and smoother, which can add to rider comfort on long journeys. The V4 is a rare find but a gem for riders who love speed and refined engineering.
Each engine configuration has its unique charm and performance quirks. Consider these features when evaluating which motorcycle engine types resonate with your personal riding style and requirements.
The Impact of Engine Type on Motorcycle Performance
Choosing the right motorcycle engine type is essential for the desired performance. Different engines offer distinct experiences and impact how a motorcycle behaves on the road. Let’s delve into how engine types affect performance.
Power and Torque Delivery
Each engine type provides a unique balance of power and torque. Single-cylinder engines deliver a straightforward power punch ideal for agile city navigation. Meanwhile, V-twins and V4s are known for strong torque at lower RPMs, favoring cruisers with their relaxed pace and powerful pull. Inline-fours scream with high-rev horsepower, giving sportbikes their swift acceleration.
Weight and Handling
Engine configuration can significantly alter a motorcycle’s weight distribution and handling. The lightweight design of single-cylinder engines makes bikes easy to handle, especially for beginners. On the other hand, boxer engines create a low center of gravity, improving stability and cornering, which is essential for adventure and touring bikes.
Vibration and Rider Comfort
Vibration levels are closely linked to engine type, affecting long-term rider comfort. Single-cylinder engines tend to vibrate more, which can be tiring on longer trips. Parallel-twins offer smoother performance with less vibration, making them ideal for everyday use. For ultimate comfort, the V4’s smoothness stands out as a top choice for long rides.
Acceleration and Speed
The desire for quick acceleration and top speed often leads riders to choose inline-four engines, which can rev high and provide a rush of speed. However, this may come at the cost of fuel efficiency. Motorcyclists looking for a balance between acceleration and economy might lean towards parallel-twin engines.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel economy is another aspect where engine type plays a vital role. Single-cylinder engines are typically more fuel-efficient, making them great for riders who prioritize economy. Conversely, high-powered engines like inline-fours and V4s may consume more fuel.
In summary, motorcycle engine types shape performance, from the thrust of torque to precision in handling and comfort on the road. Understanding these impacts is key to choosing a motorcycle engine that aligns with your performance expectations and riding lifestyle.
Advancements in Motorcycle Engine Technology

The world of motorcycles is ever-evolving, with engine technology at the forefront of innovation. Let’s explore how modern engineering has elevated motorcycle engine types to new heights.
Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
Engineers have made leaps in creating more fuel-efficient engines. Advances in injection systems and combustion processes mean that even powerful engines sip fuel more sparingly. Motorcycles can now cover more miles on less fuel, reducing both running costs and environmental impact.
Improved Emission Controls
Regulations demand cleaner engines, and manufacturers have responded. Modern motorcycles have better emission control technologies, like refined catalytic converters and advanced engine management systems. These help in minimizing the release of harmful pollutants.
Increased Power Output
High-tech materials and precision manufacturing have led to engines that are not only lighter but also stronger. This means that without increasing size, engines can produce more power and torque, enhancing the thrill of the ride with each throttle twist.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
VVT technology has crossed over from cars to motorcycles. It adjusts the timing of valve opening and closing. This optimizes performance across different RPM ranges. The result is a more responsive motorcycle at both low and high speeds.
Electronics Integration
Electronic aids are now common in motorcycle engines. Systems like traction control, riding modes, and power delivery settings are directly influenced by engine control units. These technologies offer riders a tailored experience and additional safety.
In conclusion, motorcycle engine technology has seen impressive advancements. These upgrades have enhanced the performance, efficiency, and environmental friendliness of motorcycles. With each development, riders are introduced to engines that push the boundaries of what is possible on two wheels.
Choosing the Right Engine Type for Your Riding Style
Selecting the ideal motorcycle engine type is crucial for matching your riding preferences. You must consider your riding style, the type of rides you prefer, and what performance aspects matter most to you. Let’s discuss how to align your riding needs with the right engine option.
Evaluate Your Riding Needs
First, identify your primary use of the motorcycle. If city commuting is your daily routine, single-cylinder engines offer agility and fuel efficiency. For highway cruising and long-distance comfort, a V-twin or a V4 could provide the enjoyable thrum and smooth power you seek.
Consider Power and Torque
Think about how much power and torque you need. If you’re interested in a bike that pulls strongly from a stop, look at V-twin engines. If you crave high-speed rides with rapid acceleration, inline-four engines are more suitable due to their high-revving nature.
Handling and Comfort are Key
Choose an engine that complements your desired handling dynamics. Boxer engines, for instance, might be your pick for their stability and ease in cornering. For those prioritizing a lightweight bike that’s easy to maneuver, single-cylinder engines are advantageous.
Assess Level of Experience
Are you a beginner or an experienced rider? Single-cylinder engines are less intimidating for new riders, while seasoned motorcyclists might appreciate the complexities and capabilities of inline-fours or V4s.
Factor in Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintenance should also play a role in your choice. Engines with fewer cylinders, like single-cylinder or parallel-twin engines, are typically simpler to work on. More complex engines might require professional services more often.
By taking these points into consideration, you can decide on a motorcycle engine type that fits your riding style perfectly. This choice is personal and subjective, so it’s important to weigh all factors to find your ideal match on two wheels.
More Details