Jan 27, 2026
Bouncie GPS Tracker: The Ultimate Tool for Vehicle Safety Today
Introduction
In a world where safety and convenience are paramount, the Bouncie GPS Tracker stands out as an innovative solution for vehicle monitoring and security. Designed for car owners, fleet managers, and anyone concerned about vehicle safety, the Bouncie GPS Tracker combines modern technology with user-centric features. With real-time location tracking, driving behavior analysis, and a user-friendly app, the Bouncie GPS Tracker helps people maintain a safer driving environment.

This article explores the various features, benefits, and general value of the Bouncie GPS Tracker while answering common questions. With its comprehensive offerings, the Bouncie GPS Tracker serves as an essential tool for modern vehicle safety solutions.
Understanding the Bouncie GPS Tracker
What Is the Bouncie GPS Tracker?
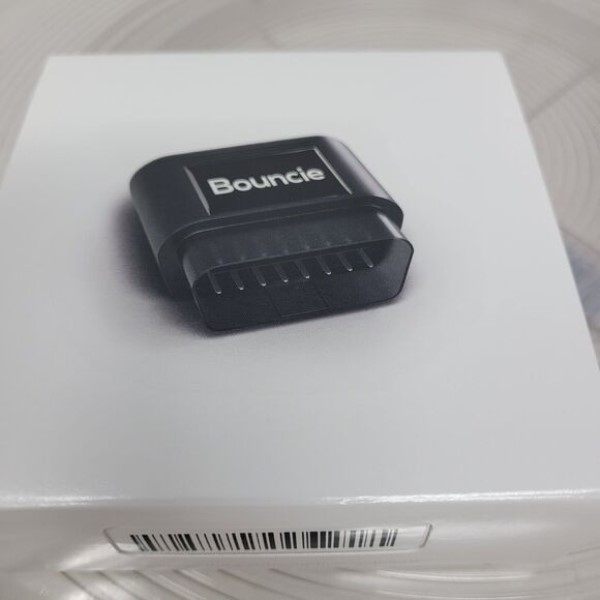
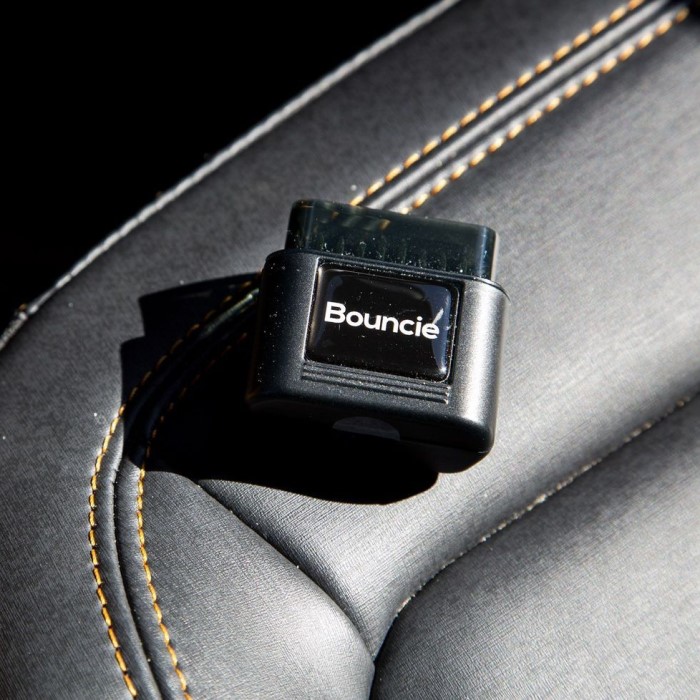
The Bouncie GPS Tracker is a compact device that plugs directly into your vehicle’s OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) port. This port is typically located under the dashboard, making installation straightforward and hassle-free. Once plugged in, the device utilizes GPS technology to provide real-time tracking and monitoring of the vehicle’s performance and location.
- Easy Installation: Installation is a breeze with the Bouncie GPS Tracker. Anyone can install it in minutes without needing professional help. Simply plug it into the OBD-II port, and it is ready to go.
- Real-Time Location Tracking: One of the standout features is real-time GPS tracking, allowing users to know exactly where their vehicle is at any moment. This feature is especially useful for monitoring parked vehicles or tracking your car during long trips.
- Performance Monitoring: Besides location services, the Bouncie GPS Tracker also provides critical data regarding vehicle performance. It tracks engine diagnostics, speed, and driving behavior, ensuring maintenance tasks are managed.
Key Features of the Bouncie GPS Tracker
The Bouncie GPS Tracker boasts several impressive features that enhance vehicle safety:
Geofencing
- Virtual Boundaries: Geofencing is a valuable feature that enables users to create virtual boundaries, often referred to as geofences, around specific locations. These zones can be customized based on personal or business needs.
- Real-Time Notifications: When the vehicle enters or exits these predefined zones, the Bouncie GPS Tracker sends instant notifications to the user’s smartphone or device. This feature allows for immediate awareness of a vehicle’s movements and is especially beneficial for those overseeing young drivers or fleet vehicles.
- Monitoring Teen Drivers: For parents, geofencing provides an added layer of safety and control. By setting up geofences around schools, homes, or other locations, parents can receive alerts when their teens arrive or leave designated areas. This capability encourages responsible driving behaviors and fosters trust between parents and teen drivers.
- Business Applications: Businesses can utilize geofencing to monitor fleet operations. For example, if a delivery vehicle leaves a specified delivery area, fleet managers receive alerts. This information helps ensure that drivers are following planned routes and enhances accountability.
Driving Behavior Analysis
- Monitoring Driving Habits: The Bouncie GPS Tracker actively monitors various driving behaviors, including hard braking, rapid acceleration, and sharp cornering. These metrics provide insight into how the vehicle is being operated.
- Data Analysis for Safety: By analyzing driving behavior data, users can identify patterns that may indicate risky driving practices. For instance, frequent hard braking could suggest aggressive driving that may increase the risk of accidents.
- Encouraging Safer Practices: Users can address identified issues through feedback and education. By encouraging safer driving habits based on the data analyzed, drivers can not only enhance their safety but potentially benefit from lower insurance rates. Insurers often offer discounts to drivers who demonstrate safe driving behaviors.
- Positive Reinforcement: In addition to identifying negative behaviors, the Bouncie Tracker can highlight good driving habits. Recognizing when a driver consistently exhibits safe driving can motivate them to continue those practices.
Maintenance Alerts
- Track Maintenance Schedules: The Bouncie GPS Tracker goes beyond location tracking by monitoring the vehicle’s maintenance needs. The device keeps records of key service intervals, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and other essential maintenance tasks.
- Proactive Notifications: Users receive notifications when it’s time to perform maintenance on their vehicles. These alerts help users stay proactive about their vehicle’s health rather than reactive to problems that arise unexpectedly.
- Preventing Breakdowns: By keeping track of maintenance schedules, users can minimize unforeseen breakdowns. Regular upkeep not only contributes to a smoother driving experience but also extends the overall lifespan of the vehicle.
- Enhancing Vehicle Value: Keeping a vehicle well-maintained increases its resale value. Regular service documented through the Bouncie Tracker provides potential buyers with confidence in the vehicle’s reliability.
Crash Detection
- Real-Time Crash Detection: One of the most critical safety features of the Bouncie Tracker is its ability to detect crashes in real time. The device is equipped with technology that can recognize when a collision occurs.
- Immediate Notifications: In the event of a crash, users receive immediate alerts through their app, allowing for quick action. This feature is vital for ensuring that help can be dispatched promptly in emergencies.
- Contacting Emergency Services: The quick notification feature enables users to contact emergency services as needed, potentially saving lives. Having the ability to respond swiftly can make a significant difference in situations where every second counts.
- Detailed Incident Reporting: After a crash, the Bouncie Tracker may provide users with a detailed report of the incident. This information can assist in insurance claims or legal matters related to the accident, further emphasizing the importance of having such a device for vehicle safety.
Benefits of Using the Bouncie GPS Tracker
Enhanced Vehicle Safety
One of the primary reasons for investing in a GPS tracker like the Bouncie is heightened vehicle safety.
- Theft Recovery: In the unfortunate event of theft, the Bouncie’s real-time location tracking feature allows law enforcement to locate your vehicle quickly. Knowing the precise location of your car significantly improves the likelihood of recovery.
- Emergency Notifications: When the device detects an accident or a problem, it sends alerts immediately. This function can be lifesaving, enabling quick response to emergencies.
Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in the Bouncie GPS Tracker can lead to financial savings in several areas:
- Insurance Discounts: Many insurance providers offer discounts for vehicles equipped with GPS systems. By having a Bouncie Tracker, you may reduce your insurance premiums, as the risk of theft is significantly mitigated.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitoring vehicle performance can prevent costly repairs down the line. By addressing issues early, you can avoid expensive breakdowns, thus saving money in the long run.
User-Friendly Application
An essential component of the Bouncie GPS Tracker is its accompanying app:
- Intuitive Interface: The app is designed to be user-friendly, allowing individuals to access important data about their vehicles quickly. Information is presented clearly, making navigation easy for users of all ages.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Users can view detailed reports regarding driving habits, location history, and vehicle diagnostics at their fingertips, empowering them with knowledge about their driving behaviors and vehicle health.
Advanced Features for Fleet Management
Benefits for Businesses
The Bouncie GPS Tracker is also a practical solution for businesses managing fleets:
- Real-Time Tracking for Fleet Vehicles: Businesses can keep track of their vehicles in real-time, improving operational efficiency and ensuring timely service for clients.
- Route Optimization: By analyzing routes and driving patterns, fleet managers can optimize delivery routes. This feature contributes to time and fuel savings, enhancing overall productivity.
- Driver Accountability: The device facilitates monitoring of driver behavior. Companies can provide feedback and training to improve safe driving practices among employees.
Customizable Alerts and Reports
- Tailored Notifications: Businesses can set custom alerts for fleet vehicles, ensuring that they are informed about any issues or deviations from scheduled routes. These alerts can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the fleet manager.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Advanced reporting features provide clear insights regarding vehicle performance, driver behavior, and fuel usage. This wealth of data empowers fleet managers to make well-informed decisions that lead to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bouncie worth it?
For many users, the Bouncie GPS Tracker offers substantial value. Enhanced safety, real-time tracking, driving habit analysis, and maintenance alerts all contribute to a compelling case for its worth. Many customers report high satisfaction levels due largely to the peace of mind they gain.
Does Bouncie tracker work when the car is off?
Yes, the Bouncie GPS Tracker functions even when the vehicle is powered off. While you may not receive live updates during this time, you can access the last known location and monitor any unauthorized movements.
Does Bouncie GPS require a subscription?
Indeed, Bouncie GPS requires a subscription. After purchasing the device, users must opt for a monthly plan to utilize features such as real-time tracking, diagnostics, and alerts through the app.
Conclusion
In summary, the Bouncie GPS Tracker is indeed the ultimate tool for vehicle safety today. Featuring real-time tracking, driving behavior monitoring, and maintenance alerts, it offers comprehensive solutions for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your vehicle. Whether you’re a concerned parent, daily commuter, or a fleet manager, the Bouncie GPS Tracker provides peace of mind through state-of-the-art technology.
As vehicle technology continues to advance, having a reliable GPS tracker like Bouncie becomes essential for safeguarding your investment and enhancing your driving experience. Investing in a Bouncie GPS Tracker allows you not only to monitor your vehicle but also to embrace a culture of safety and proactive maintenance. By adopting this modern device, you’ll stay informed, prepared, and in control of your vehicle’s safety and performance. Explore the possibilities that the Bouncie GPS Tracker offers and take the first step toward a safer tomorrow!
More Details